The Xinomavro of the Kamkoutis Estate conquered the top
T ο Ξ ι ν ό μ α υ ρ ο τ ο υ Κ τ ή μ α τ ο ς Κ α μ κ ο ύ τ ΤΗ κ α τ έ κ τ ΤΗ σ ε τ ΤΗ ν κ ο ρ υ φ ή
At the 25th Thessaloniki Wine & Spirits Trophy, Xinomavro from the Kamkouti Estate took the top spot. Xinomavro (Xinomavro), vintage 2021, received the Special Distinction in dry single-varietal wine, from the homonymous variety, while also winning the Gold Medal 2025, as it was rated 95.00/100.00.
In total, five of the estate's six labels received distinctions, with the local Tsapournako, vintage 2021, and the red Kourites, vintage 2020, being awarded a Silver Medal, while the white Kourites, vintage 2024, and the estate's Malagouzia 2024 will now be able to carry the Bronze Medal symbol.
Ktima Kamkouti, an up-and-coming and quality winery, reminds us why Velvento and its vineyards deserve a special place on the wine map of the country. And their "thank you" to the critics and to all those who enjoy their production will always be enclosed in their bottles.
The Thessaloniki Wine & Spirits Trophy 2025 International Competition
With a passion for the art of wine and the magic of distillation, the Thessaloniki Wine & Spirits Trophy 2025 competition highlighted excellence in the world of wine and spirits for yet another year.
Thirty distinguished tasters—Masters of Wine, Master Sommeliers, oenologists, sommeliers and respected wine journalists—coming from Greece and abroad, met in six committees and evaluated 1,030 samples from Greece and Cyprus.
Top wines and spirits will now carry the distinguished medal sticker, Gold, Silver or Bronze.
Under the presidency of Master of Wine Konstantinos Lazarakis, the institution continues to be a benchmark for the quality and authenticity of Greek wine. A bottle with the symbol of the White Tower on its seal is not just a choice; it is the guarantee that you are holding in your hands a product that has earned the appreciation of the industry's leaders.
Fermentation Process
Crushing is the process when gently squeezing the berries and breaking the skins to start to liberate the contents of the berries. Destemming is the process of removing the grapes from the rachis (the stem which holds the grapes). In traditional and smaller-scale wine making, the harvested grapes are sometimes crushed by trampling them barefoot or by the use of inexpensive small scale crushers.
These can also destem at the same time. However, in larger wineries, a mechanical crusher/destemmer is used. The decision about destemming is different for red and white wine making. Generally when making white wine the fruit is only crushed, the stems are then placed in the press with the berries. The presence of stems in the mix facilitates pressing by allowing juice to flow past flattened skins. These accumulate at the edge of the press.
On occasion, the winemaker may decide to leave them in if the grapes themselves contain less tannin than desired. This is more acceptable if the stems have ‘ripened’ and started to turn brown. If increased skin extraction is desired, a winemaker might choose to crush the grapes after destemming.
Wine is one of the most civilized things in the world and one of the most natural things of the world that has been brought to the greatest perfection, and it offers a greater range for enjoyment and appreciation than, possibly, any other purely sensory thing.
Ernest Hemingway Tweet
Removal of stems first means no stem tannin can be extracted. In these cases the grapes pass between two rollers which squeeze the grapes enough to separate the skin and pulp, but not so much as to cause excessive shearing or tearing of the skin tissues. In some cases, notably with “delicate” red varietals such as Pinot noir or Syrah, all or part of the grapes might be left uncrushed (called “whole berry”) to encourage the retention of fruity aromas through partial carbonic maceration.
The Grapes
The quality of the grapes determines the quality of the wine more than any other factor. Grape quality is affected by variety as well as weather during the growing season, soil minerals and acidity, time of harvest, and pruning method. The combination of these effects is often referred to as the grape’s terroir.
Grapes are usually harvested from the vineyard from early September until early November in the northern hemisphere, and mid February until early March in the southern hemisphere.
In some cool areas in the southern hemisphere, for example Tasmania, harvesting extends into May. The most common species of wine grape is Vitis Vinifera, which includes nearly all varieties of European origin. The most common species of wine grape is Vitis Vinifera, which includes nearly all varieties of European origin.
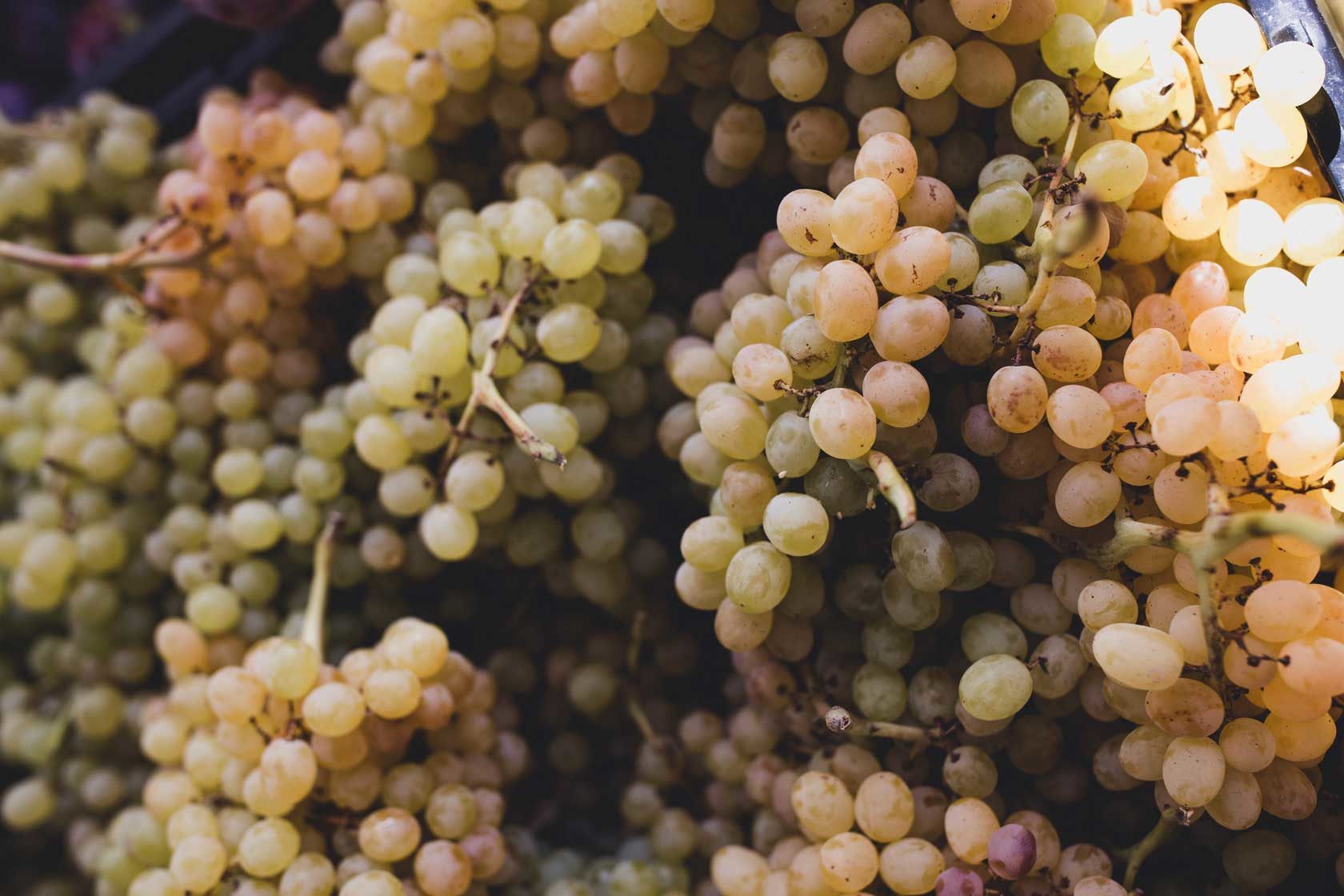

Manual harvesting is the hand-picking of grape clusters from the grapevines. In the United States, some grapes are picked into one- or two-ton bins for transport back to the winery. Manual harvesting has the advantage of using knowledgeable labor to not only pick the ripe clusters but also to leave behind the clusters that are not ripe or contain bunch rot or other defects. This can be an effective first line of defense to prevent inferior quality fruit from contaminating a lot or tank of wine.
Destemming is the process of separating stems from the grapes. Depending on the winemaking procedure, this process may be undertaken before crushing with the purpose of lowering the development of tannins and vegetal flavors in the resulting wine. Single berry harvesting, as is done with some German Trockenbeerenauslese, avoids this step altogether with the grapes being individually selected.
Crushing is the process when gently squeezing the berries and breaking the skins to start to liberate the contents of the berries. Destemming is the process of removing the grapes from the rachis (the stem which holds the grapes).
In traditional and smaller-scale wine making, the harvested grapes are sometimes crushed by trampling them barefoot or by the use of inexpensive small scale crushers. These can also destem at the same time. However, in larger wineries, a mechanical crusher/destemmer is used. The decision about destemming is different for red and white wine making. Generally when making white wine the fruit is only crushed, the stems are then placed in the press with the berries. The presence of stems in the mix facilitates pressing by allowing juice to flow past flattened skins.

Katerina Monroe
@katerinam • More Posts by Katerina
Congratulations on the award, it's well deserved! You guys definitely know what you're doing. Looking forward to my next visit to the winery!